Explore Socotra Island, a biodiversity hotspot in the Indian Ocean, known for its unique flora and fauna, offering a rare and extraordinary natural experience.
Nestled in the Arabian Sea, off the coast of Yemen, Socotra Island is one of the most unique and biologically diverse places on Earth.
Often described as the “Galápagos of the Indian Ocean,” this isolated island is home to an array of plant and animal species found nowhere else in the world.
Also Read
Socotra’s distinctive landscape, shaped by millennia of isolation, is a living testament to the wonders of evolutionary adaptation.
This article explores the island’s fascinating biodiversity, its geographical significance, and why Socotra is a must-visit destination for nature lovers and adventurers alike.
An Island of Extraordinary Flora and Fauna
Socotra Island is a true natural wonder, with over 800 species of plants and animals, a third of which are found nowhere else on the planet.
The island’s isolation for around 20 million years has allowed species to evolve in unique ways, resulting in a highly specialized ecosystem that has earned Socotra its place as a UNESCO World Heritage site.
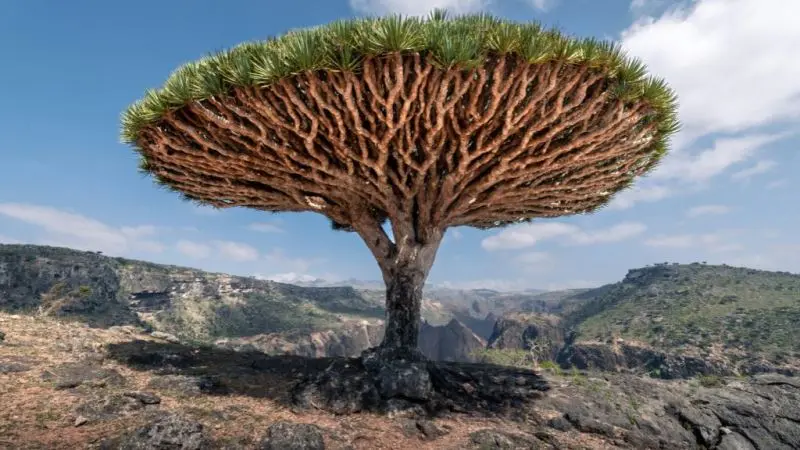
Flora: One of the island’s most famous plants is the Dragon’s Blood Tree (Dracaena cinnabari), which has a distinct umbrella-shaped canopy and produces a red resin that has been used for centuries in medicine, dyes, and incense.
The tree’s peculiar appearance, along with its ability to thrive in the harsh environment of Socotra, makes it a symbol of the island’s biodiversity.
Other endemic plants include the Socotran fig tree (Ficus socotrana) and the Socotran cucumber (Cucumis melo), both of which have adapted to the island’s arid conditions.
Many of these species are found only on Socotra and its surrounding islets, making them crucial to the island’s fragile ecosystem.
Fauna: Socotra is also home to a wide variety of unique animal species. The island is known for its endemic reptiles, including the Socotran chameleon and the Socotran skink, both of which are adapted to the island’s desert-like environment.
Birdwatchers will find Socotra a haven, with endemic species like the Socotra starling and the Socotra bunting, both of which have evolved to thrive in the island’s unique ecosystem.
The island’s marine life is equally impressive, with coral reefs surrounding Socotra that are home to a variety of fish, sea turtles, and marine mammals, making it a top destination for divers.
A Geography Shaped by Isolation
Socotra’s biodiversity can be attributed to its unique geographic location and isolation.
The island is located approximately 350 kilometers from the Arabian Peninsula and 1,500 kilometers from the Horn of Africa, placing it in a strategic position between Africa and the Arabian world.
This isolation has created an environment where species could evolve with little influence from outside factors.
The island’s topography is equally diverse, with rocky mountains, vast deserts, and lush valleys that provide a range of microclimates.
This variety in habitats has allowed for the development of multiple ecosystems within a relatively small area, further contributing to Socotra’s biodiversity.
The island is also subject to extreme weather conditions, with hot temperatures, strong winds, and seasonal rains. Despite these harsh conditions, the flora and fauna of Socotra have adapted in remarkable ways.
For example, the Dragon’s Blood Tree has developed its unique umbrella shape to provide shade and minimize water loss, while the island’s animals are often nocturnal to avoid the intense daytime heat.
A Unique Ecosystem: Natural Adaptations
The isolation of Socotra has led to fascinating evolutionary adaptations. Many of the plants and animals on the island have developed specialized traits that allow them to thrive in the harsh and arid environment.
For example, the island’s flora often has thick, fleshy leaves or stems that store water, while many of its animals have evolved to be nocturnal or burrowing to escape the intense daytime heat.
Socotra’s plants also demonstrate extreme adaptations to conserve water. The Socotran desert rose (Adenium obesum), for example, has a swollen stem that stores water for long periods of drought.
Other plants, like the Socotran vine (Cissus quadrangularis), are able to climb and spread quickly, allowing them to take advantage of available space in the challenging environment.
In terms of animal life, the island’s reptiles have developed camouflage abilities that allow them to blend into their surroundings.
The Socotran chameleon, for instance, has the ability to change color to match the environment, making it well camouflaged against the island’s rocky and sandy landscapes.
Socotra: A Living Laboratory for Scientists
Due to its biodiversity, Socotra Island is of significant interest to biologists and scientists around the world.
The island serves as a living laboratory for studying evolutionary processes and understanding how species adapt to isolated environments.
Many researchers come to Socotra to study the island’s plants and animals, gaining insights into the mechanisms of adaptation, speciation, and survival in harsh environments.
The uniqueness of Socotra’s ecosystem also makes it a prime location for conservation efforts.
As climate change and human activity continue to threaten biodiversity worldwide, Socotra stands as a reminder of the delicate balance of nature and the importance of protecting vulnerable ecosystems.
Efforts are underway to preserve Socotra’s natural habitats and protect its endemic species from the dangers of habitat destruction and invasive species.
Cultural Significance and Local Communities
While Socotra is primarily known for its biodiversity, it also has a rich cultural heritage. The island is home to the Socotri people, a group with their own language, traditions, and customs.
The Socotri language, which is a member of the Semitic language family, is spoken by the majority of the island’s population, and many Socotri traditions are tied to the land and the natural environment.
The local people have a deep connection to the island’s plants and animals, with many species used in traditional medicine, food, and daily life.
For example, the Dragon’s Blood Tree has been used by the Socotri people for its resin, which is believed to have healing properties.
Despite the island’s remote location and challenges, the Socotri people continue to live in harmony with their environment, practicing sustainable farming and fishing methods that have been passed down through generations.
However, modern challenges, including limited access to healthcare and education, have made life on Socotra increasingly difficult.
Conservation Challenges and the Future of Socotra
Socotra’s unique ecosystem and cultural heritage are under threat due to climate change, overgrazing by livestock, and the introduction of invasive species.
The increasing pressures of tourism and development have also contributed to the challenges facing the island’s biodiversity.
Efforts are underway to protect Socotra’s delicate environment. In addition to being a UNESCO World Heritage site, the island is part of the Yemen Ministry of Environment’s conservation program, which aims to preserve its natural resources and promote sustainable tourism.
Researchers and conservationists are also working with the local communities to raise awareness about the importance of protecting the island’s biodiversity and traditional ways of life.
Despite these efforts, the island’s future remains uncertain. However, the global attention Socotra has garnered in recent years has helped bring more resources and awareness to the island’s conservation needs.
As tourism increases, there is a growing focus on developing sustainable tourism practices that allow visitors to appreciate the island’s beauty without harming its fragile ecosystem.
Socotra Island is a biodiversity paradise that offers a glimpse into the evolutionary wonders of the natural world.
Its unique plants, animals, and ecosystems, coupled with its isolation, make it a rare and invaluable destination for nature lovers, researchers, and adventurers alike.
While the island faces significant conservation challenges, its rich biodiversity and the efforts to protect it underscore the importance of preserving such extraordinary places.
Whether you are a scientist, a traveler, or someone who simply appreciates the beauty of nature, Socotra is a place unlike any other, a true treasure of the Indian Ocean.